Before installing additional power wiring, or when replacing or repairing wiring in cars and other vehicles, questions appear on the correct selection and use of the wire required for installation.
Content
- Wiring car and fire safety, what conditions must be observed?
- Tables of operational characteristics of cable and wires of domestic manufacturers
- Cable imported production
- What is the difference in the marking of the import and domestic cable?
- How to choose a cable cross section what you need to know?
- Example of calculating the cable cross section for a car
- Requirements for connections and insulation of electrical wiring, connectors and tips
- Autotractor Wires, Pros and Cons
- Tips Prof.
Wiring car and fire safety, what conditions must be observed?
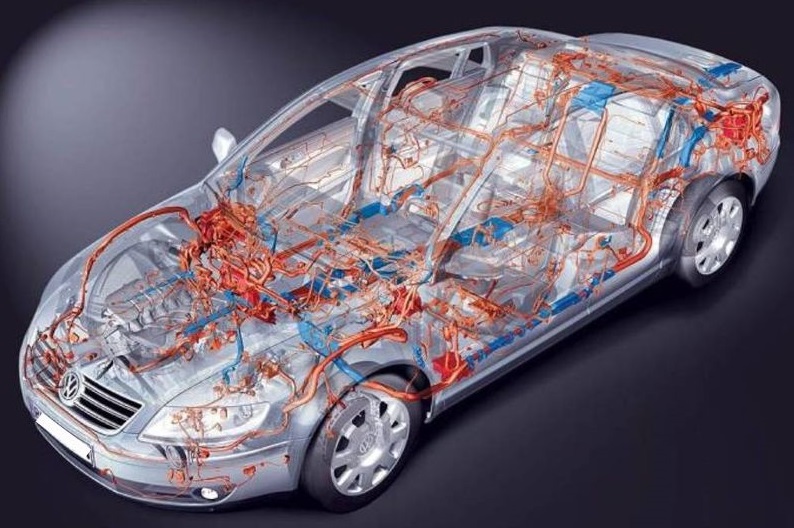
When choosing cables and wires in the first place, fire safety requirements are facing. In the car body, the wiring has to be laid on the thresholds and corners through random suitable holes and bulkheads. The wires during operation are influenced by low and high temperatures, fuel, oil, acids, water, ice, as well as shaking, vibration, friction, shocks and other destructive factors.
It is important to know that in the summer time the temperature in the car, which stands with closed glasses in the sun, in medium latitudes is capable of reaching +60 degrees Celsius, and in the south +90 degrees. In winter, in a strong frost, the temperature of the vehicle in medium latitudes can reach -40 degrees Celsius, in Siberia and in the Urals up to -60 degrees, and in Yakutia to -70 degrees Celsius.
It is dangerous to use a rigid wiring with unreliable insulation, which is easily cracking. Such a wire can cause short circuit and fire. Cables and wires must be applied to the location of their current installation, as well as on operational and climatic conditions.
It is important that the wire be flexible and has a solid insulation, which does not soften when heated and does not duby at minus temperatures. As for the conductive cable veins, it must be a multi-breeding and copper, and should also make a nominal current. In conditions of current overloading of the chain and short circuit, before the fuse flashes the fuse in the circuit fuse, the conductive vein (conductor) should not be heated to the melting point of the cable insulation. If the fire for some reason arose, the insulation of the wiring should not spread the fire.
Tables of operational characteristics of cable and wires of domestic manufacturers
The domestic cable industry produces a wide range of wires that are suitable for power wiring in the vehicle.
| Cable | Section MM. 2 | Purpose | Operating temperature | Insulation |
| PVZ. | 0,5.95 | Installation | - 50 ° C. + 70 ° С | PHV plastic |
| PVKV. | 0,75.120 | Output | - 60 ° C. + 180 ° С | Rubber |
| PVEP-M. | 2,5…70 | Power | - 60 ° С ... + 100 ° С | Rubber |
| Powes. | 0,5…6,0 | Transport | - 40 ° С ... + 105 ° С | PHV plastic |
| PGVA | 0,5…95 | AutoTractor | - 60 ° С ... + 70 ° С | PHV plastic |
| Plow | 0,5…95 | AutoTractor | - 40 ° С ... + 105 ° С | PHV plastic |
| NV, NVM. | 0,5…2,5 | Mounting | - 50 ° С ... + 105 ° С | PHV plastic |
Cable imported production
Foreign industry produced special cables and wires for power wiring cars. These cables are ideally responsible to them. They are distinguished by a translucent shell of brown or red and a specific weaving of conductive veins consisting of beams of wires, returned among themselves.
In low-cost cables, the wires are made of simple copper, more expensive - from oxygen-free, reducing reduced resistance and, as a result, lower losses.
What is the difference in the marking of the import and domestic cable?
Imported cables have typical marking, for example:
- Power Cable- This is a power cable.
- ProLeader, Belsis -brand brand of manufacturer or supplier.
- OFC -wire made of oxygen-free copper.
- # 20 - NR20 - NO20 - №20- Size (i.e. caliber) conductive veins.
- BWG -Birmingham Wire Sort.
- AWG - American sorting.
- SWG -Standard sorting.
The wires of one caliber in various sortments are insignificantly different in the diameter of the veins (wires). AWG's sortment is the main for the power wiring of the car.
| Caliber, AWG. | Analog, mm. 2 | Resistance, OM / M | Cross section, mm. 2 | Diameter mm. |
| 0000 | 95.0 | 0.00018 | 107.2 | 11.68 |
| 000 | 95.0 | 0.00023 | 85.0 | 10.41 |
| 00 | 70.0 | 0.00029 | 67.5 | 9.27 |
| 1/0 | 50.0 | 0.00037 | 53.5 | 8.25 |
| 1 | 35.0 | 0.00047 | 42.4 | 7.35 |
| 2 | 35.0 | 0.00057 | 33.6 | 6.54 |
| 3 | 25.0 | 0.00073 | 26.68 | 5.83 |
| 4 | 25.0 | 0.00091 | 21.15 | 5.19 |
| 5 | 16.0 | 0.0012 | 16.8 | 4.62 |
| 6 | 16.0 | 0.0014 | 13.3 | 4.12 |
| 7 | 10.0 | 0.0018 | 10.55 | 3.67 |
| 8 | 8.0 | 0.0024 | 8.37 | 3.26 |
| 9 | 6.0 | 0.0031 | 6.63 | 2.91 |
| 10 | 5.0 | 0.0036 | 5.26 | 2.59 |
| 11 | 4.0 | 0.0046 | 4.17 | 2.31 |
| 12 | 3.0 | 0.0054 | 3.31 | 2.05 |
| 13 | 2.5 | 0.0074 | 2.62 | 1.83 |
| 14 | 2.0 | 0.0088 | 2.08 | 1.63 |
| 15 | 1.5 | 0.012 | 1.65 | 1.45 |
| 16 | 1.5 | 0.015 | 1.31 | 1.29 |
| 17 | 1.00 | 0.018 | 1.04 | 1.15 |
| 18 | 0.75 | 0.023 | 0.82 | 1.02 |
| 19 | 0.75 | 0.025 | 0.65 | 0.91 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 0.035 | 0.52 | 0.81 |
How to choose a cable cross section what you need to know?
To select a cable caliber you need to know:
- The length of the cable from the load to the battery.
- The greatest current consumed by the load.
- Rated voltage of AKB or other source that are intended for power supply.
The wire must have such a thickness (cross section) of the conductor, in which the reduction of the voltage on the cable resistance with a long-term (maximum) current consumption is no more than 10 percent of the rated voltage of the AKB. With a short-term (pulse) current consumption, a voltage reduction is allowed to 15 percent.
If the battery has a voltage of + 12V, then the maximum allowable voltage decrease should be not more than + 1.2V (in the pulse + 1.8V). Side network voltage + 12V have gasoline cargo and passenger cars, light diesel cars and buses. Voltage + 24V have heavy buses and trucks, and also diesel SUVs.
Reducing the voltage on the resistance of the cable is caused by the power excretion and the heating of the conductor. Since the conductor of the wire is in the insulating shell, it prevents it in cooling. To reduce heating, you need to choose a conductor cross-section, given the current density coefficient, which for different wire laying conditions can be 1-10 A / mm2.
Example of calculating the cable cross section for a car
You can find out the greatest current consumed by the load, at a nominal fuse inserting the load fuse or by the amount of the fuse values, when the loads are somewhat. You can also determine the greatest current according to the formula Ims \u003d P: 6, if you know the output power of UNG.
For example, we calculate the caliber of the wire if the load of the battery + 12V is the sound power amplifier 2x200W output. As for the distance between the battery and the amplifier, it is 6 meters.
Payment:
Load capacity 2x200w \u003d 400w
The largest current 400w: 6 \u003d 67a
Wire section 67 A: 6 A / mm2 \u003d 11.2 mm2
The wire, which is close to section 11.2 mm2, is a wire of caliber number 7 AWG with a cross section of 10 mm
This wire caliber has six meters resistance of the conductor (see table): 6 m x 0.0018 Ohm \u003d 0.001 Ohm
Conducting voltage on wire conductor: 67 A x 0.0011 Ohm \u003d 0.74 V. This is 7.4 percent of the voltage + 12V.
From this calculation it follows that the seventh caliber wire is selected correctly.
The cross section of conductive conductors is determined by the formula: S \u003d D 2/ 4, where D is the diameter of the vein, and \u003d 3.14.
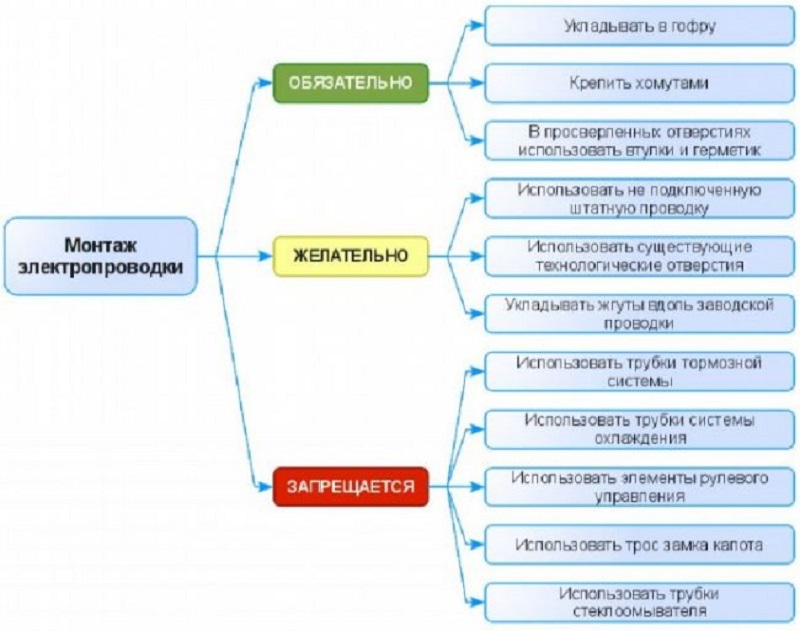
Requirements for connections and insulation of electrical wiring, connectors and tips
To prevent the short circuit of the power cable to the ground, you need to install a fuse holder on the "plus" wire. It is recommended to put a "flask" type holder. It is characterized by a characteristic transparent sealed body and makes it possible to clamp the cable to caliber No.000. It is established in the rupture of the wire near the "plus" terminal of the AKB. It is important that the housing of the fuse holder was securely fixed.
The quantity of fuse inserting the fuse insertion should be selected by 20-30 percent more than the highest current consumed. The cable from the load to the fuse should be from one piece (one dimensional segment), since the compounds worsen reliability and can cause voltage loss in conditions of high power consumption. If for some reason still have to connect the wires, then for their splicing it is necessary to use special "car" couplings or distributors with an isolated housing made from heat-resistant plastic, and reliable clamping contacts.
If special coupling products are missing, you can use mounting boxes, terminal blocks and pads for household and industrial wiring. It is impossible to use insulating PVC tape in the form of an insulator of the spliced \u200b\u200bends of the wire. If you need to set the tip to the wire for the bolted contact connection, clean the wire from insulation and put the tip on it with the inner diameter of the shank, which corresponds to the wire caliber. Next, you need to enhance the shank with a special tool, and the location of the crimp is called.
During the cable laying, it is recommended to avoid damage, place the wire in the corrugated tube of the corresponding diameter. If the cable passes through areas with sharp edges, you need to pass the wiring through nylon or rubber seals, that is, wipers.
You need to connect the load and battery with two oily cables with the same conductive core and insulation of different color. It is forbidden to apply metal chassis or vehicle body in the form of a "minus" feed wire, since due to bad contact compounds and welds, it is possible to reduce the load supply voltage.
During the assembly of the car body, the body elements and chassis are connected with the help of welding, threaded connections and rivets. These compounds provide galvanic contact between individual parts of the mechanical structure and its rigidity, and for power currents they form body transient total resistance.
Autotractor Wires, Pros and Cons
Autotractor wires are used in electrical wiring of different vehicles:
- Combines.
- Tractors.
- Motor scooters and mopeds.
- Buses.
- Cars of various tonson.
PVGA and PVA wire brands are used to connect electrical equipment and devices with different nominal voltage. Such devices are mounted on vehicles, which is designed for use in cold, moderate and tropical climates. Withstand a high temperature scatter, which reaches 100 degrees.
Autotractor wires PVA, PWAM and PGWA are single-core wires with high flexibility. Thermal vein is made of copper. From above, the cable is coated with polyvinyl chloride insulation - a solid or combined coloring. Cables are heat-resistant, their service life is at least ten years.
Also wires in this category:
- Do not spread burning.
- Not susceptible to cracking.
- Resistant to the effects of mold fungi.
- Neutral to the influence of motor oils, gasoline and diesel fuel.
- The assembly bends of their properties are saved.
Tips Prof.
We recommend to see the following video:
Related Materials
- Stove 2110, bad warm stove 2110, VAZ 2110 heating system, repairing the heating system VAZ 2110 with their own hands
- VAZ 2114 stove blows with cold air, stove 2114, bad warm stove VAZ 2114, device and repair of heating VAZ 2114 do-it-yourself, removing the stove VAZ 2114
- How to subdominize the car. How to put a jack. Types of jacks for cars.
- VAZ 2109 Fuse Block, VAZ 2109 Fuse Block Carburetor, VAZ 2109 Fuse Block Injector, Old VAZ 2109 Fuse Block, VAZ 2109 Fuse Block, VAZ Fuse Block 2109
- Car exhaust gas catalyst, faulty catalyst, pluses and cons of the catalyst, how to change the catalyst for the planeencitel
- Stove blowing cold air VAZ 2114, badly blowing the stove VAZ 2114, why badly blowing the stove VAZ 2114
- How to find out the owner of the car by the number of his car, check the car by the number of the traffic police machine, check the car by the state number of the car for free
- How to choose Used tires, Useful Tips
- Winter car road, pressure in passenger car tires in winter, good battery for the car in winter, whether to warm the car in winter
- In winter, the car is poorly started. How to make a car in winter, do you need to warm up the car in winter, useful tips
- Economy fuel consumption machines, the most economical car consumption
- Tires brands for passenger cars, labeling of car tire labeling, residual passenger car tire protector, how to pick a tire on a car brand, car tire tread pattern
- Working transmission operation, mechanical gearbox clutch work, driving with manual gearbox, useful tips
- Rear beam Peugeot 206 sedan, rear beam device Peugeot 206. Rear beam Peugeot 206 Malfunction, repair of the rear beam Peugeot 206
- Diesel fuel in winter, additive for diesel fuel in winter, how to choose the best diesel fuel
- Diesel winter does not start. How to start diesel in winter, heating diesel in winter.
- Japanese bridgestone tires, winter studded bridgestone tires, bridgestone tires brand
- Tire marking decoding for passenger cars, labeling wheels, how to choose the right tires on the disks
- Diesel engine in winter, launch of the diesel engine in winter, what oil to fill in a diesel engine in winter, useful tips
- LED backlight of the car, the backlight of the bottom of the car, the backlight of the legs in the car, the backlight in the door of the car, the backlight of the car is fine
- Recovered tires, bus tire, restored tire protector, can I use them
- Choose winter tires, which is a winter tires, which pressure in winter tires should be marked with winter tires, how to choose the right winter tires, the best winter tires 2019
- Steering rail rail, knock of steering rack, reasons for the knock and repair of the steering rack do it yourself
- Cameless car tires, a set for repair of tubeless tires, repair of the cannon-free tire do it yourself
- Russian tires, Russian tires Winter, Russian All-season tires, Voronezh AMTEL tires, Tires "Matador Omsk Tire", Kama-tires are world-class bus
- How to open a car without a key. Lost the key from the car what to do, the key from the car inside the car
- Silent tires, quiet winter tires, quiet studded bus, which tires to choose, overview tires
- Tires and safety, safety of the bus, why it is necessary to constantly monitor car tires
- Rules of safe driving of the car in the rain and slush, safe driving of the car for beginners
- Rust converter which is better for cars, rust converters to choose how to use rust transducer, professionals
- Polishing the body of the car do it yourself, how to choose a polishing paste, useful tips
- Engine durability, engine life, how to extend engine life
- Knock in the car. Knock when moving the car. What can knock in the car. How to determine the cause of the knock.
- ABS car, what is ABS car, ABS system malfunction, ABS diagnostics
- Overtaking a car when you can start overtaking a car, rules of traffic rules
- Fuel pump VAZ 2110, VAZ 2110 gas station scheme, VAZ 2110 fuel pump device, VAZ 2110 gas station repair,
- Automotive antennas for radio, automotive antenna device, car antenna do it yourself
- Front suspension Kalina, device front suspension Kalina, knock in front suspension Kalina, repair of front suspension Kalina
- Shock absorber Oil, best oil shock absorbers, pumping oil shock absorbers, how to properly pump oil shock absorber
- Clutch malfunctions, touches clutch, causes a clutch malfunction, how to eliminate











Comments