The first all-wheel drive transport appeared at the beginning of the 20th century. These were passenger cars, the purpose of which is to participate in race off-road and highway. By the invention, the audience was cooled and such cars did not get distribution. It seemed that the idea was died, however, at the beginning of the last century, the designers reanimated it by developing cargo all-wheel drive cars. And here the developers had a question - how to distribute the torque between the leading bridges. It was clear that the standard gearbox would not solve this problem. After a number of manipulations, a completely new unit appeared, which will be discussed in this article.
Content
- Dispensing box that she distributes why she is a dispensing box
- Dressing box device
- Distribution box, types of dispensing boxes
- Disposal boxes and their purpose
- Viscounts for blocking (dignity and disadvantages)
- Differential Torsen Self-locking mechanism (device, advantages and disadvantages)
- Friction multidisk coupling as a blocking mechanism (principle of operation, dignity and disadvantages)
- Chain gear
Dispensing box that she distributes why she is a dispensing box
All-wheel drive transport, in contrast to the monotrifer, is equipped with such a device as a dispensing box. Its purpose is the correct distribution of torque between the axes of the car, as well as its increase to the passage of labor-free places (not on all vehicles).
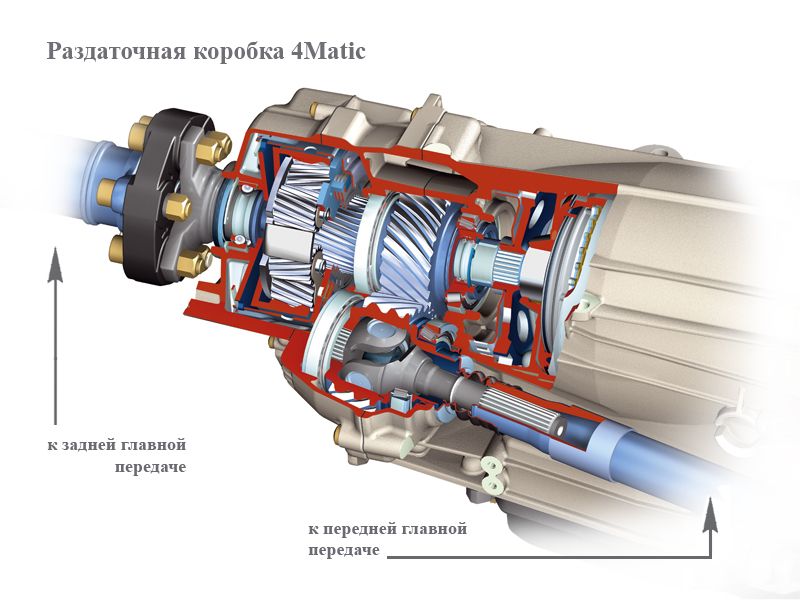
The dispensing box is installed after the gearbox or separate unit, and sometimes, and one with a gearbox.
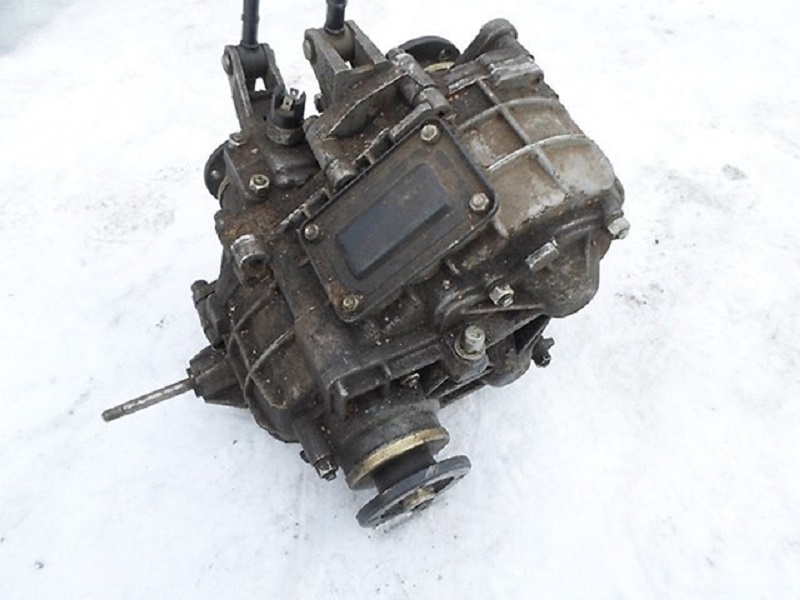
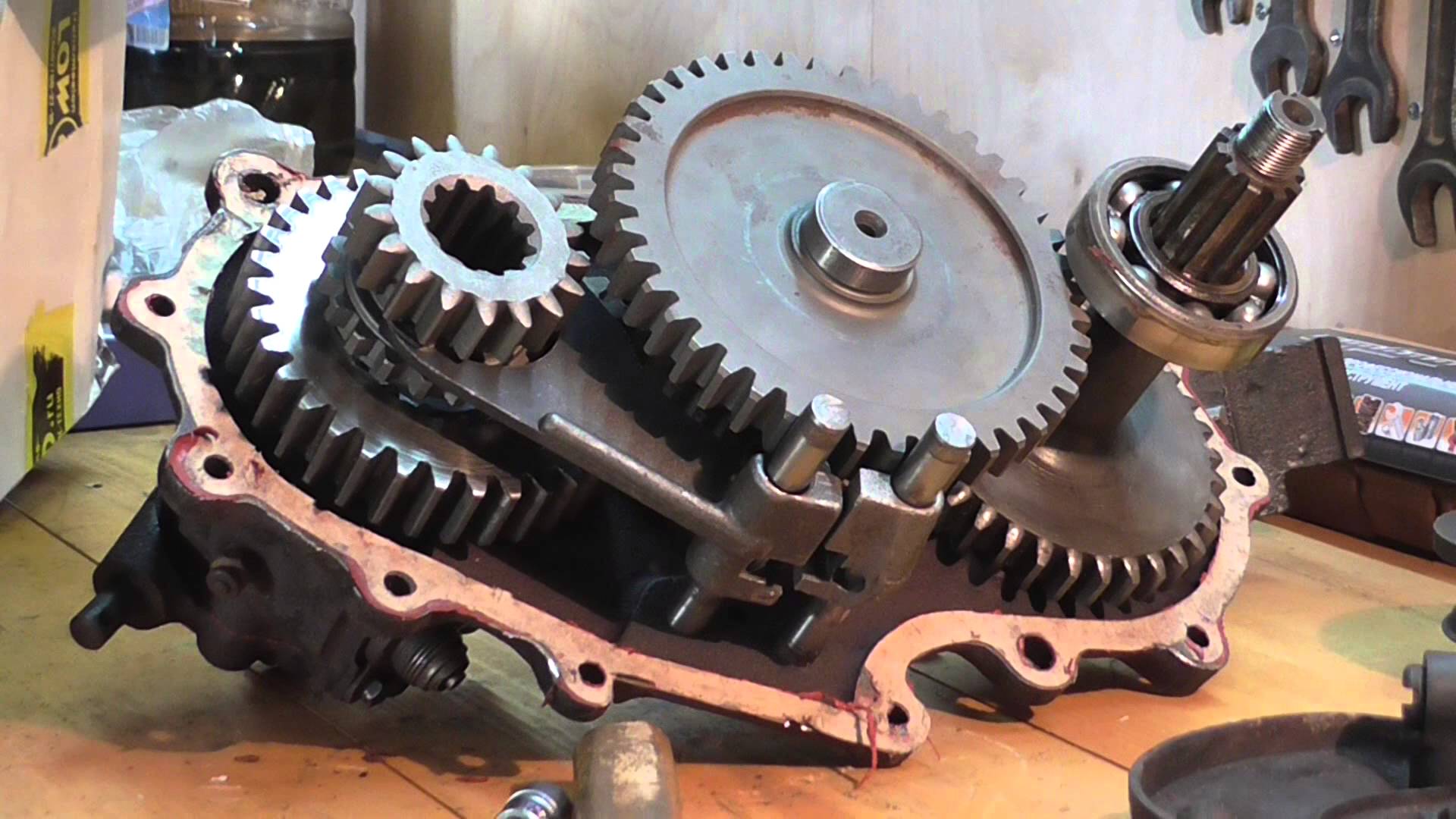
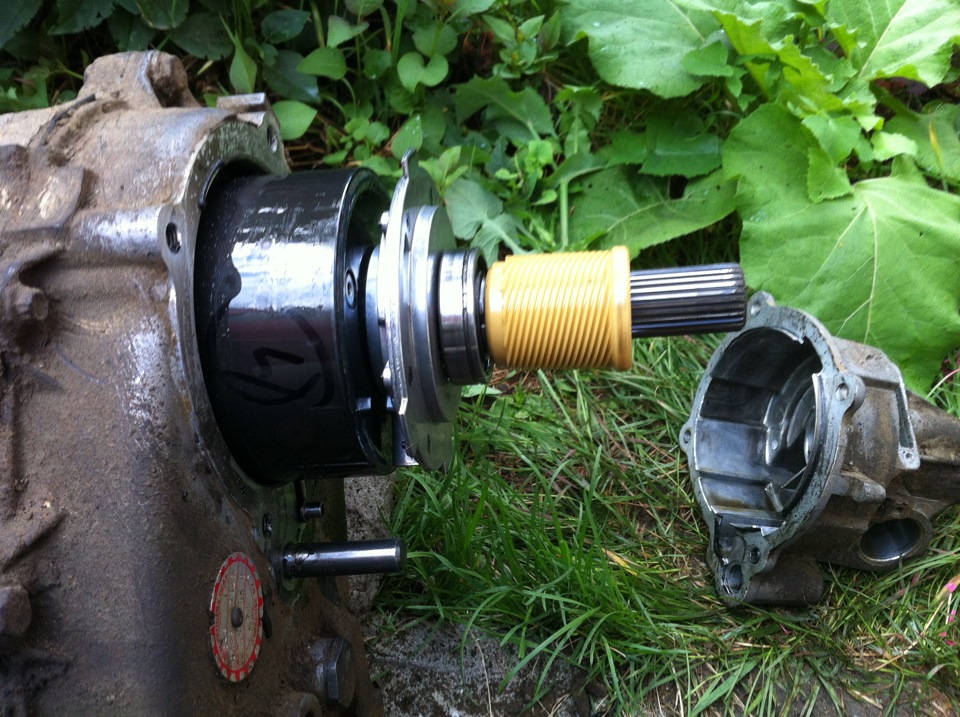
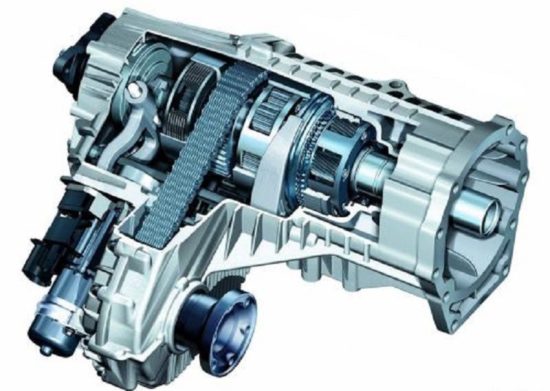
Dressing box device
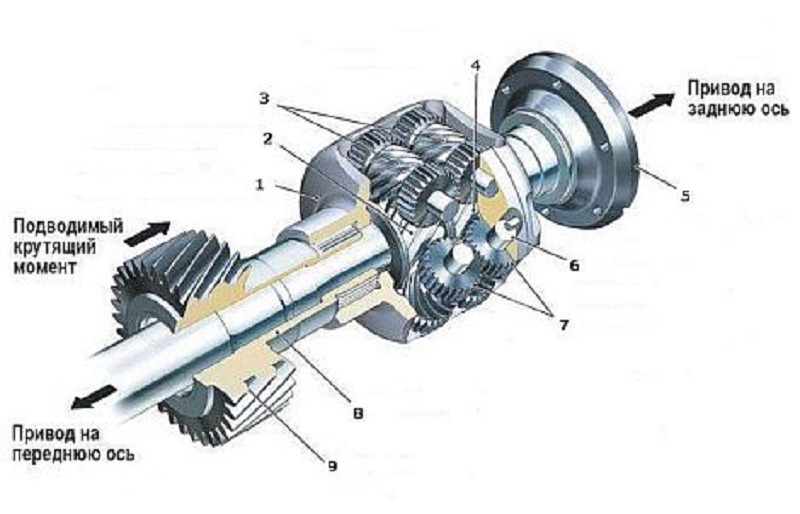
The design "Distribution" may differ depending on the type of the full drive system, however, you can note the general structural elements of the "Distribution":

- Drive shafts for rear and front axles.
- Lead shaft.
- Seamless or chain transmission.
- Lowering either downstream.
- Inter-seed differential.
- The mechanism of blocking the mid-scene differential.

Distribution box, types of dispensing boxes
According to the modern classification, there are such variations of dispensing boxes:
- On the placement of drive shafts (with unauthorized and coaxial shafts).
- By type of drive leading bridges (blocked or differential drive).
- By number of gears (single-stage, two-stage and three-stage).

Disposal boxes and their purpose
Consider more appointment of various nodes of "Distribution".
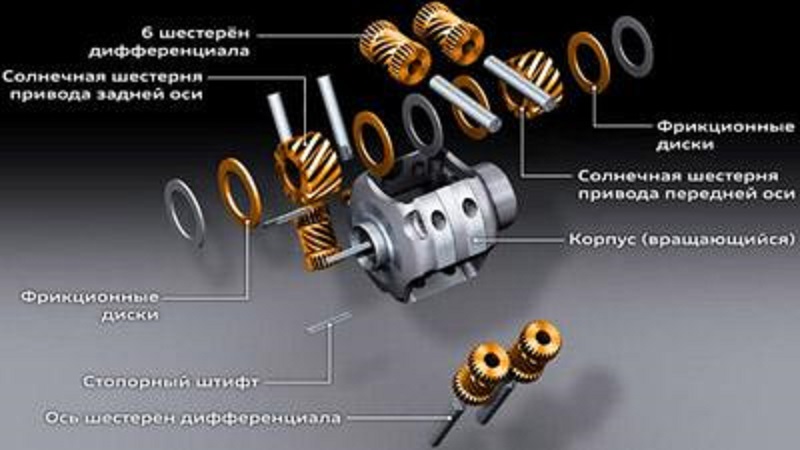
inter-seed differential (purpose, species)
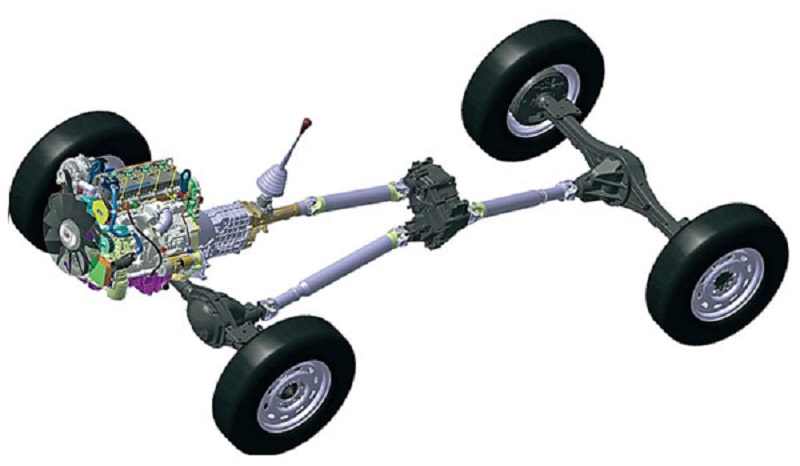

This node is responsible for the distribution of the mid-sieve torque and allows the drive shaft to be revisted at various angular velocities, which is particularly important while driving, since the wheels pass different distances and, as a result, should rotate at different speeds. If "Distribution" is not equipped with such a node, then to provide the wheels with the possibility of rotation at different speeds can be possible only by disconnecting one axis.
It is worth noting that the inter-axis differentials are symmetrical and asymmetrical. The latter works so that the torque is divided into a certain proportion, and the first one gives it equal to two axes.
blocking Mechanism of Mechanical Differential (Types and Purpose)
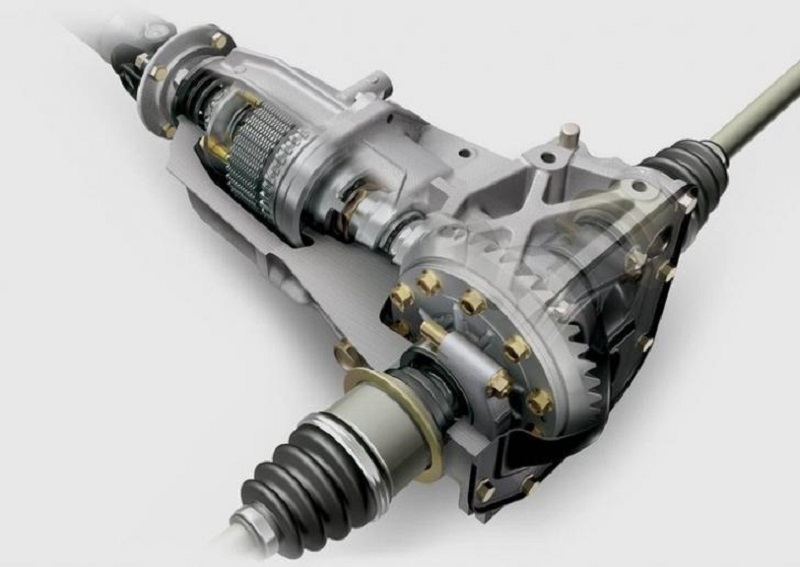

For a full-fledged sale by a car of its off-road opportunities, the inter-axis differential is equipped with a locking mechanism, the purpose of which is based on forcibly forcing the wheels of both axes to rotate with a uniform speed. Depending on the variation of the mechanism, the blocking can occur or forcibly or manually.

To date, these types of locks are applied:
- Viscosity coupling (Viscounts).
- Differential self-locking Torsen.
- Friction multidisk coupling.
Viscounts for blocking (dignity and disadvantages)

This is the easiest device that allows you to automatically block the inter-sieve differential. Her principle of action is: inside the Viscounts, perforated discs are immersed in silicone fluid, some discs are connected to the housing, while others - with the hub. During the slip of the wheels of one of the axes, part of the disks begins to rotate faster than others, and the silicone fluid, warming up, thick, as if gluing the housing with the hub.
The main advantage of this system is low cost. Minuses are much greater: the triggering is carried out with the receipt, which is why the vehicle can break through the axle wheels; from long work the system overheats; Differential lock is not complete; Such a node is incompatible with the ABS system.
Differential Torsen Self-locking mechanism (device, advantages and disadvantages)
This design consists of a set of worm gears - slaves and leading. The principle of operation of this device is: if all the wheels are "kept" the road normally, the differential equalizer gives the axes torque. However, when one of the axes begin to slip, the moment is moved to another axis, thanks to the strength of friction in worm gear. The ratio of effort sometimes comes to 20:80. The main disadvantage of such a solution is restrictions on the strength of the structure. Therefore, Torsen is not mounted on SUVs, its lots are crossovers.
Friction multidisk coupling as a blocking mechanism (principle of operation, dignity and disadvantages)
This is a set of friction discs that have a controlled compression ratio. Such a coupling makes it possible to distribute the moment between axes depending on the conditions of the area. If these conditions are usual, the torque is divided equally. During the slip of one of the axes, coupling discs occurs, and the differential is blocked partially either completely. To ensure work, the coupling is equipped with an electronic control system and hydraulic or electric drive. The inter-semicircle differential can also be blocked by manually by electrical, hydraulic, pneumatic or mechanical drive. Many cars have the ability to block differential or automatically or manually.
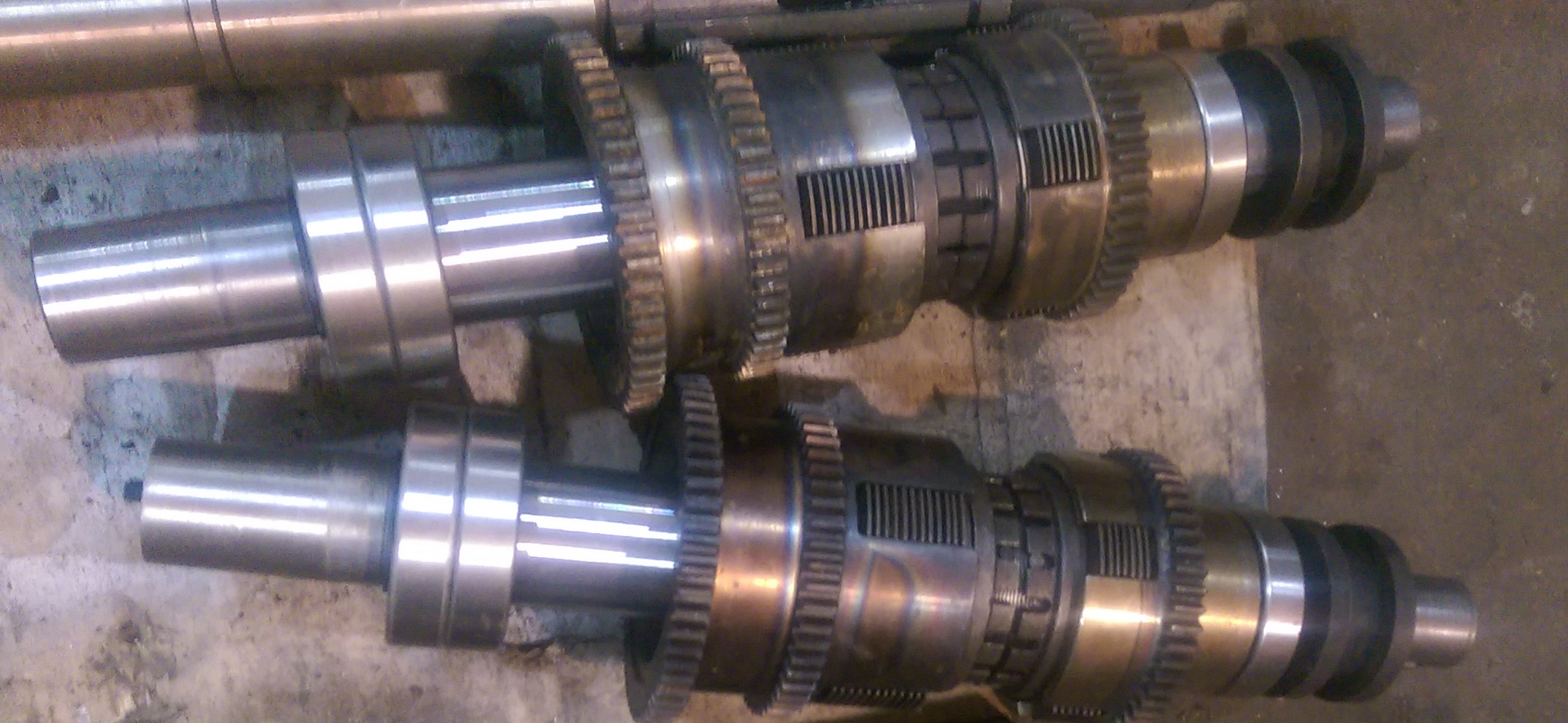
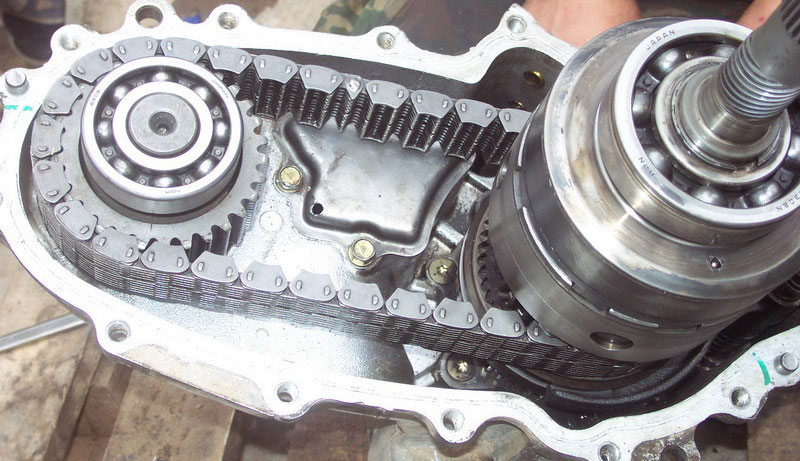
Chain gear
The purpose of this node is based on the transmission of torque on the driving shaft of the front axle of the vehicle to ensure the performance of the full drive. It consists of a drive chain and a pair of gear wheels (slave and leading). In addition to the chain transmission, the "distribution" is sometimes used toothed, which consists of cylindrical gears.
Related Materials
- Stove 2110, bad warm stove 2110, VAZ 2110 heating system, repairing the heating system VAZ 2110 with their own hands
- VAZ 2114 stove blows with cold air, stove 2114, bad warm stove VAZ 2114, device and repair of heating VAZ 2114 do-it-yourself, removing the stove VAZ 2114
- How to subdominize the car. How to put a jack. Types of jacks for cars.
- VAZ 2109 Fuse Block, VAZ 2109 Fuse Block Carburetor, VAZ 2109 Fuse Block Injector, Old VAZ 2109 Fuse Block, VAZ 2109 Fuse Block, VAZ Fuse Block 2109
- Car exhaust gas catalyst, faulty catalyst, pluses and cons of the catalyst, how to change the catalyst on the planeencitel
- Stove blowing cold air VAZ 2114, badly blowing the stove VAZ 2114, why badly blowing the stove VAZ 2114
- How to find out the owner of the car by the number of his car, check the car by the number of the traffic police machine, check the car by the state number of the car for free
- How to choose Used tires, Useful Tips
- Winter car road, pressure in passenger car tires in winter, good battery for the car in winter, whether to warm the car in winter
- In winter, the car is poorly started. How to make a car in winter, do you need to warm up the car in winter, useful tips
- Economy fuel consumption machines, the most economical car consumption
- Tires brands for passenger cars, labeling of car tire labeling, residual passenger car tire protector, how to pick a tire on a car brand, car tire tread pattern
- Working transmission operation, mechanical gearbox clutch work, driving with manual gearbox, useful tips
- Rear beam Peugeot 206 sedan, rear beam device Peugeot 206. Rear beam Peugeot 206 Malfunction, repair of the rear beam Peugeot 206
- Diesel fuel in winter, additive for diesel fuel in winter, how to choose the best diesel fuel
- Diesel winter does not start. How to start diesel in winter, heating diesel in winter.
- Japanese bridgestone tires, winter studded bridgestone tires, bridgestone tires brand
- Tire marking decoding for passenger cars, labeling wheels, how to choose the right tires on the disks
- Diesel engine in winter, launch of the diesel engine in winter, what oil to fill in a diesel engine in winter, useful tips
- LED backlight of the car, the backlight of the bottom of the car, the backlight of the legs in the car, the backlight in the door of the car, the backlight of the car is fine
- Recovered tires, bus tire, restored tire protector, can I use them
- Choose winter tires, which is a winter tires, which pressure in winter tires should be marked with winter tires, how to choose the right winter tires, the best winter tires 2019
- Steering rail rail, knock of steering rack, reasons for the knock and repair of the steering rack do it yourself
- Cameless car tires, a set for repair of tubeless tires, repair of the cannon-free tire do it yourself
- Russian tires, Russian tires Winter, Russian All-season tires, Voronezh AMTEL tires, Tires "Matador Omsk Tire", Kama-tires are world-class bus
- How to open a car without a key. Lost the key from the car what to do, the key from the car inside the car
- Silent tires, quiet winter tires, quiet studded bus, which tires to choose, overview tires
- Tires and safety, safety of the bus, why it is necessary to constantly monitor car tires
- Rules of safe driving of the car in the rain and slush, safe driving of the car for beginners
- Rust converter which is better for cars, rust converters to choose how to use rust transducer, professionals
- Polishing the body of the car do it yourself, how to choose a polishing paste, useful tips
- Engine durability, engine life, how to extend engine life
- Knock in the car. Knock when moving the car. What can knock in the car. How to determine the cause of the knock.
- ABS car, what is ABS car, ABS system malfunction, ABS diagnostics
- Overtaking a car when you can start overtaking a car, rules of traffic rules
- Fuel pump VAZ 2110, VAZ 2110 gas station scheme, VAZ 2110 fuel pump device, VAZ 2110 gas station repair,
- Automotive antennas for radio, automotive antenna device, car antenna do it yourself
- Front suspension Kalina, device front suspension Kalina, knock in front suspension Kalina, repair of front suspension Kalina
- Shock absorber Oil, best oil shock absorbers, pumping oil shock absorbers, how to properly pump oil shock absorber
- Clutch malfunctions, touches clutch, causes a clutch malfunction, how to eliminate









Comments