Today, most cars on the roads are equipped with any type of anti-lock brake system. Let's see what this system consists and how it works.
Principle of operation abs
Initially, consider the basic principle of operation of the ABS system.
Since different manufacturers have their own versions of ABS, their specifications and parts may be called differently.
The ABS is a system that works with all four wheels, which prevents them in blocking, automatically changing the pressure in the brake system of each wheel during emergency braking.
Preventing wheel lock, the system, firstly, allows the driver to continue driving a car, and secondly, can cut the brake path.
During the usual braking of the system with ABS and without ABS, the same is equally for the driver.
During the same braking, when operating ABS on brake pedals, you can feel the pulsation, which is accompanied by the vibration of the brake pedal and characteristic sound.
Device ABS car
Cars with ABS are equipped with a pedal drive with a double brake system.
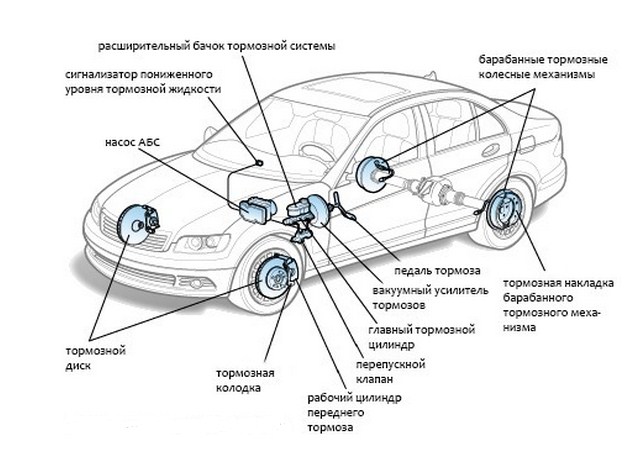
The main hydraulic brake system consists of:
- hydraulic control valve and electronic control unit.
- the main brake cylinder
- brake tubes and hoses
- brake cylinders on each wheel.
The anti-lock system consists of the following components:
- hydraulic control unit
- electronic Block ABS
- the front and rear sensors of the anti-lock system.
How the ABS car works
The anti-lock system works as follows:
When you click on the brake pedal, it presses on the liquid in the main brake cylinder And as a result, the liquid is squeezed out from there under pressure.
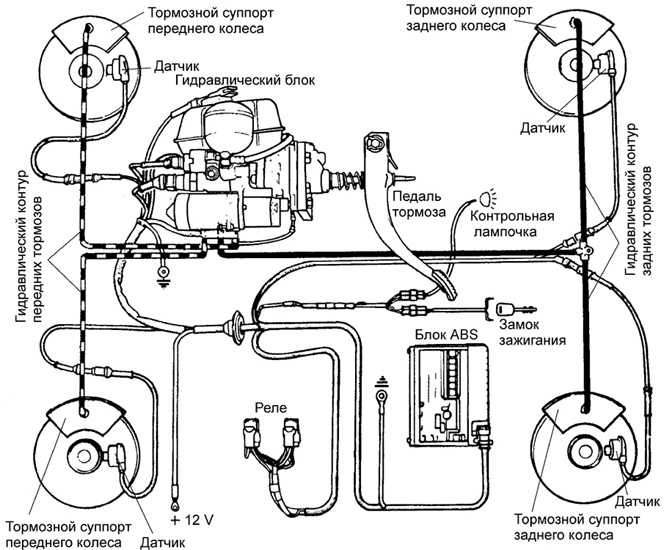
From the main brake cylinder, the liquid enters the hydraulic control unit ABS.
In the hydraulic control unit there are 4 outputs, each of which is connected by a tube with a brake cylinder on the wheel.
At each of these outputs of the hydraulic unit of the ABS, the valve is opened in the original state.
The pressure fluid is pushed out of the hydraulic control unit and on the tubes and hoses enters the brake cylinders on each wheel.
In the brake cylinder, pressure is created on the wheel, and the liquid pushes the piston, which is associated with brake pads.
As a result, the brake pads are powered by a brake disc or drum. Because of this, friction force arises between the brake pads and the brake disc, and it slows down its rotation.
Accordingly, its rotation slows down and the wheel.
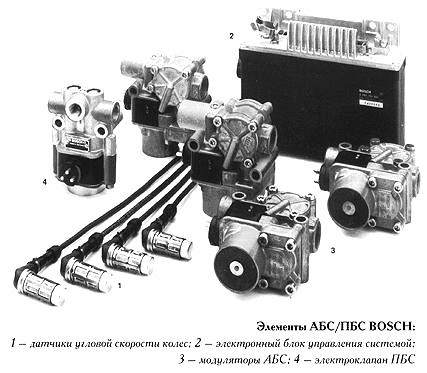
In the brake systems of equipped ABS on the hub of each wheel, a toothed disk and a sensor are fixed.
When rotating the disk teeth wheel passing near the sensor, which fixes it.
The data from the sensor is transmitted to the electronic control unit.
With a very sharp braking, the wheel can also be blocked and the sensor for slowing the rotation of the wheel will notice this.
As a result, the electronic control unit of the ABS seeing that some wheel was blocked, the signal to the hydraulic control unit and blocks the valve supplying the brake fluid to this wheel.
Since the pressure of the brake fluid is reduced to this wheel, it stops slowing down and starts rotating again.
As soon as the wheel begins to rotate, the valve on the hydraulic unit opens, and the pressure of the brake fluid is again transmitted to the brake system of this wheel.
The wheel begins to slow down again.
These actions are repeated very quickly and manifest themselves to the driver in the very characteristic sound and vibration of brake pedal when pressed.
Due to this, when braking the wheels are not blocked and the car does not go, as it is called a yuz.
After all, when driving, the car becomes unmanaged and does not respond to steering. ABS also avoids this and saves the driver with the ability to control the car.
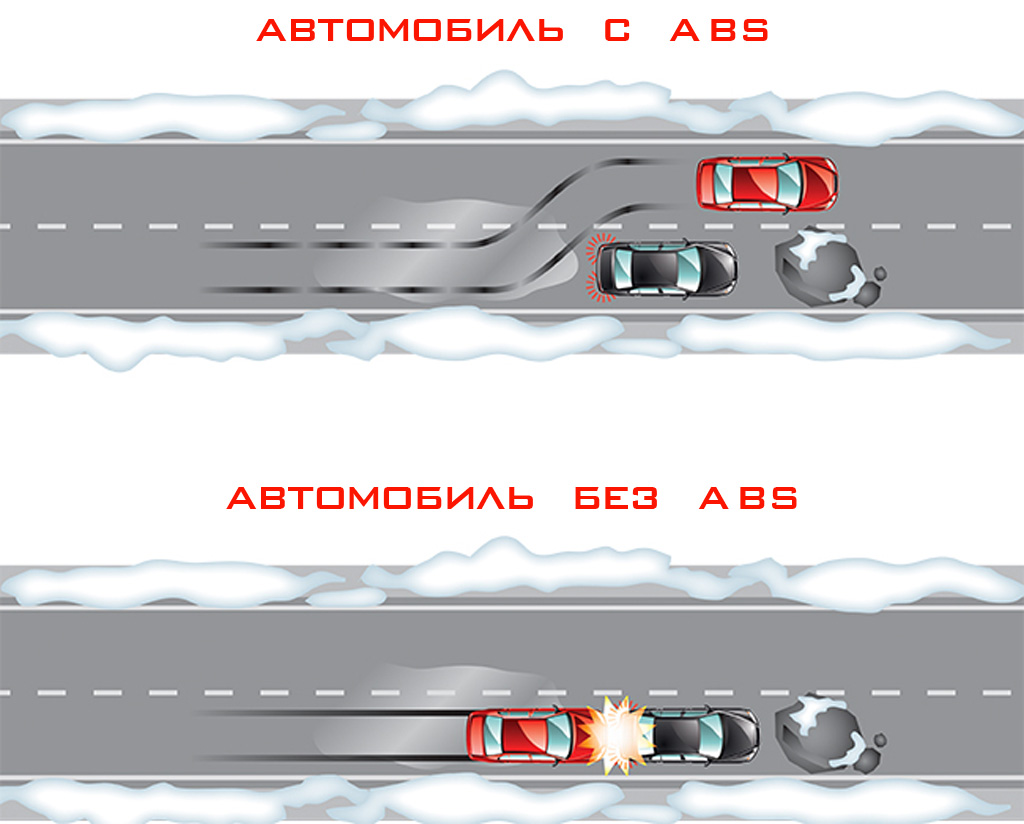
For example, it will help to drive around the obstacle, not letting the brake pedals. There is a delusion that cars equipped with an ABS system stop at a shorter distance than cars without ABS. In reality, it is often not true.
The car with the ABS in most cases will pass a bigger way to a complete stop, but due to the fact that the driver can drive a car he can drive around the obstacle, and not just helplessly press the brake pedal and hope that the car will stop on time.
Also, the ABS system has a positive effect on the tire tread state. After all, in the absence of ABS and when blocking the wheel in braking, the tire will be drown on asphalt only by one point.
As a result of such braking, the tire can be very stealing in one place. During the operation of the ABS, this does not occur.
This is a description of the simplified principle of operation of the ABS system.
In practice, the design of the brake system and the ABS is much more complicated. For example, the brake system of the modern car has at least two independent contours.
This means that the front and rear wheels are controlled by separate tubes from the main brake cylinder.
It helps to keep the ability to slow down the car, even when one of the brake tubes will receive damage.
Tip from professional
ABS in different manufacturers can differ significantly.
In addition, this system can be very difficult and demanding for servicing and repairing greater experience and special tools. Therefore, an inexperienced driver should not be attempts to independently fix the ABS, and it is better to contact the specialists.
Related Materials
- Stove 2110, bad warm stove 2110, VAZ 2110 heating system, repairing the heating system VAZ 2110 with their own hands
- VAZ 2114 stove blows with cold air, stove 2114, bad warm stove VAZ 2114, device and repair of heating VAZ 2114 do-it-yourself, removing the stove VAZ 2114
- How to subdominize the car. How to put a jack. Types of jacks for cars.
- VAZ 2109 Fuse Block, VAZ 2109 Fuse Block Carburetor, VAZ 2109 Fuse Block Injector, Old VAZ 2109 Fuse Block, VAZ 2109 Fuse Block, VAZ Fuse Block 2109
- Car exhaust gas catalyst, faulty catalyst, pluses and cons of the catalyst, how to change the catalyst on the planeencitel
- Stove blowing cold air VAZ 2114, badly blowing the stove VAZ 2114, why badly blowing the stove VAZ 2114
- How to find out the owner of the car by the number of his car, check the car by the number of the traffic police machine, check the car by the state number of the car for free
- How to choose Used tires, Useful Tips
- Winter car road, pressure in passenger car tires in winter, good battery for the car in winter, whether to warm the car in winter
- In winter, the car is poorly started. How to make a car in winter, do you need to warm up the car in winter, useful tips
- Economy fuel consumption machines, the most economical car consumption
- Tires brands for passenger cars, labeling of car tire labeling, residual passenger car tire protector, how to pick a tire on a car brand, car tire tread pattern
- Working transmission operation, mechanical gearbox clutch work, driving with manual gearbox, useful tips
- Rear beam Peugeot 206 sedan, rear beam device Peugeot 206. Rear beam Peugeot 206 Malfunction, repair of the rear beam Peugeot 206
- Diesel fuel in winter, additive for diesel fuel in winter, how to choose the best diesel fuel
- Diesel winter does not start. How to start diesel in winter, heating diesel in winter.
- Japanese bridgestone tires, winter studded bridgestone tires, bridgestone tires brand
- Tire marking decoding for passenger cars, labeling wheels, how to choose the right tires on the disks
- Diesel engine in winter, launch of the diesel engine in winter, what oil to fill in a diesel engine in winter, useful tips
- LED backlight of the car, the backlight of the bottom of the car, the backlight of the legs in the car, the backlight in the door of the car, the backlight of the car is fine
- Recovered tires, bus tire, restored tire protector, can I use them
- Choose winter tires, which is a winter tires, which pressure in winter tires should be marked with winter tires, how to choose the right winter tires, the best winter tires 2019
- Steering rail rail, knock of steering rack, reasons for the knock and repair of the steering rack do it yourself
- Cameless car tires, a set for repair of tubeless tires, repair of the cannon-free tire do it yourself
- Russian tires, Russian tires Winter, Russian All-season tires, Voronezh AMTEL tires, Tires "Matador Omsk Tire", Kama-tires are world-class bus
- How to open a car without a key. Lost the key from the car what to do, the key from the car inside the car
- Silent tires, quiet winter tires, quiet studded bus, which tires to choose, overview tires
- Tires and safety, safety of the bus, why it is necessary to constantly monitor car tires
- Rules of safe driving of the car in the rain and slush, safe driving of the car for beginners
- Rust converter which is better for cars, rust converters to choose how to use rust transducer, professionals
- Polishing the body of the car do it yourself, how to choose a polishing paste, useful tips
- Engine durability, engine life, how to extend engine life
- Knock in the car. Knock when moving the car. What can knock in the car. How to determine the cause of the knock.
- ABS car, what is ABS car, ABS system malfunction, ABS diagnostics
- Overtaking a car when you can start overtaking a car, rules of traffic rules
- Fuel pump VAZ 2110, VAZ 2110 gas station scheme, VAZ 2110 fuel pump device, VAZ 2110 gas station repair,
- Automotive antennas for radio, automotive antenna device, car antenna do it yourself
- Front suspension Kalina, device front suspension Kalina, knock in front suspension Kalina, repair of front suspension Kalina
- Shock absorber Oil, best oil shock absorbers, pumping oil shock absorbers, how to properly pump oil shock absorber
- Clutch malfunctions, touches clutch, causes a clutch malfunction, how to eliminate







Comments